| Radio-Frequency Circuits > Target Radio-Frequencies |
Wireless communication systems require specific radio-frequency integrated circuits, which often require optimum performances. The radio-frequency integrated circuits have to deal with traditional requirements such as low power consumption or high speed, but also with low process variation influence, power efficiency, linearity, low temperature influence, and low noise sensitivity.
| Application | GSM | DECT | UMTS | Bluetooth | IEEE 820.11a | IEEE 820.1b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Mobile phone 1st generation |
Mobile phone 2nd generation |
Mobile phone 3rd generation |
Wireless network |
Very high rate wireless networking |
High rate wireless networking |
| Frequency (MHz) | 890-915 |
1880-1900 |
1910-2200 |
2450 |
5200 |
2450 |
| Data rate | 12Kb/s |
100Kb/s |
0.1-2Mb/s |
0.72-10Mb/s |
6-18Mb/s |
1-5Mb/s |
| Output Power | 1-2 Watts |
100mW |
1 watt |
100mW |
0.1-1 Watt |
0.1-1 Watt |
Modern radio frequencies equipments operate at frequency ranges officially called ultra-high frequencies (UHF) ranging from 300MHz to 3GHz, and super high frequencies (SHF) ranging from 3GHz to 30GHz. The "HF" bandwidth designates the bandwidth 3-30MHz. Mobiles phones and wireless networking have been the driving applications of radio-frequency integrated circuits, as described in the figure 12-1.
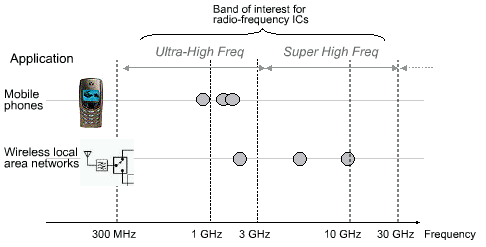 |
| Figure 12-1. Some key radio-frequency applications |
| Radio-Frequency Circuits > Target Radio-Frequencies |